An HTTP response communicates a web server’s status to a browser or search engine. It includes status codes (200, 301, 404, 500), headers, and content, helping diagnose loading issues, redirections, or server errors for better SEO performance.
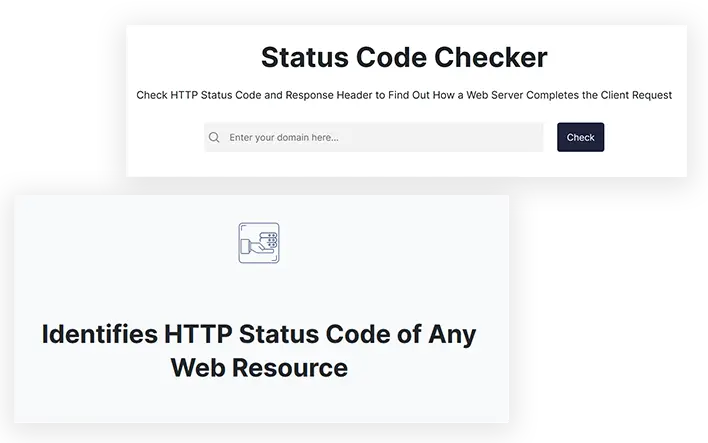
Status Code Checker
Check HTTP Status Code and Response Header to Find Out How a Web Server Completes the Client Request
Features
.svg)
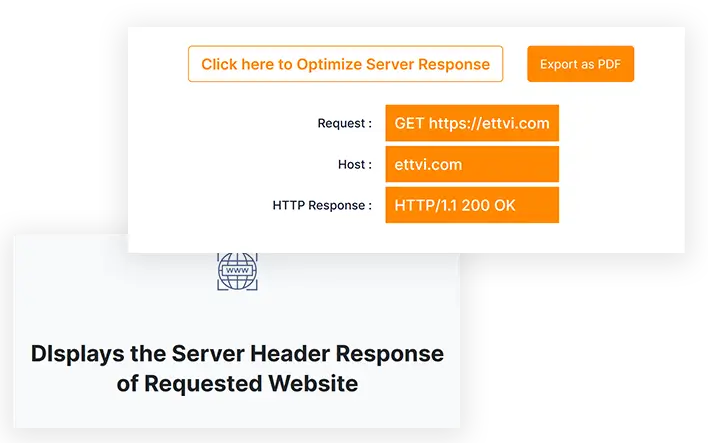
Identifies HTTP Status Code of Any Web Resource

DIsplays the Server Header Response of Requested Website

Processes Multiple URLs to Check Server Status In Bulk
Related Tools
ETTVI’s Status Code Checker
ETTVI’s Status Code Checker enables the tracking of all the information about a web server, including its http/https status code and response header. The webmasters can leverage it to troubleshoot the web server issues and make sure that their web resources load properly.
Enter multiple URLs to check web server status, http/https response code, and server header information in bulk.
With this advanced tool, the webmasters can easily check the informational (100, 101), redirection (301, 302), and success (200) response codes of any web server - just the way required. ETTVI’s Status Code Checker tool serves the best to detect errors in the server response.
Use ETTVI’s multi-featured Status Code Checker to check the status code, response time, IP address, content type, content length, and set cookies of any web server - for free of cost.
How to Use ETTVI’s Status Code Checker?
STEP 1 “Enter URL(s)”
Write or paste single or multiple URLs in the “Text Box” as per the requirement.
For example - https://ettvi.com/
STEP 2 “Run the Tool”
Click on “Check” to run ETTVI’s Status Code Checker.
STEP 3 “Check Results”
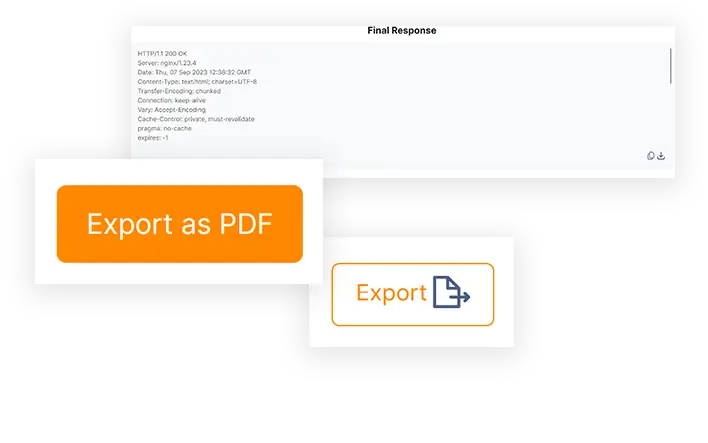
ETTVI’s Status Code Checker will process the requested URL https://ettvi.com/ and display the following results:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Why Use ETTVI’s Status Code Checker?
ETTVI’s Status Code Checker makes it easy to check how well the server of a web resource responds when an internet user requests to access and load it.
It highlights all the status codes, including information, redirect, and success. The webmasters can use it to detect the http error codes (client and server errors) to know how to troubleshoot the server issues of any website.
Its user-friendly interface works efficiently to process the given URL(s) and display the following:
- Server Status
- HTTP Response Code
- HTTP Header
All the webmasters can easily find how the web server completes the client’s request to load a web resource with ETTVI’s advanced ETTVI’s Status Code Checker - for free of cost.
Quick Guide to Status Code
HTTP status codes act as brief messages from the server that are tacked onto a web page. They’re not part of the site's content at all. Instead, you'll get server logs informing you of the status of your request to see a certain page.
What is the Status Codes for HTTP Requests?
When a browser requests an HTTP status code, the server responds to it with that status code. Requests from your browser are sent to a server, which then responds with a three-digit code, known as the HTTP status code, in response.
In order to minimize downtime on your site, it’s important to know how to use status codes. Using these status codes, your browser and the server may communicate with each other across the Internet. They tell each other if things are going well or if there is a problem between them. These status codes can even help both search engines and users find your site like 301 redirect tells bots and users that the page has been permanently relocated.
Each three-digit status code starts with one of five digits from 1 to 5, represented as 1xx or 5xx to signify that range. All the server responses fall into one of these ranges.
HTTP Status Code Classes:
- Informational responses (1xxs): The server is pondering the request.
- Achieved success (2xxs): The request was successfully completed, and the server responded to the browser with the information as expected.
- Redirection (3xxs): You have been redirected to another website. The request was successfully received, but there was some sort of redirection.
- Client Errors (4xxs): Page Could Not Be Located It was not possible to reach the website or page. A request was performed, but the page was not valid – this is an error on the website's end of things, and it arises frequently when a page does not exist on the site.
- Errors on the server (5xxs): Failure Despite the fact that the client submitted a valid request, the server could not finish the request.
Important Status Codes for SEOs:
Every professional SEO and website owner should understand the status codes that have the most impact on SEO.
If you are working on a site displaying a lot of 5xx errors, you will want to know right away that this is a server issue. Right away, consider any modifications you have made to your URLs or deleted pages because 4xx mistakes have a negative impact on your visitors' experience. 301 redirects and custom 404 pages can be used to redirect users to the correct location after knowing the root cause of the problem.
There are a few status codes that every SEO should know, and they are worth memorizing:
100 - Server Code
“Normal operation” is represented by 100. There was a valid request, and the server began processing it. After sending the last data packet, the user receives this temporary response code. When can I use this code? A user may already have received data from the server. Thus this code is not generated.
101 - Switching Protocols
One of the most uncomplicated server codes, meaning the user requested a change in web server protocol, which the server granted.
When can this code be used? When upgrading from an older HTTP version. If a better protocol exists, this one is used.
102 - Processing
The request time might be extended with several subqueries and file operations in a WebDAV request (transfer protocol).
When is this code valid? As a result of the lengthy request processing time, this code is generated to alert the user to reset the timer and wait for the following command.
Status Code 200 – OK
Normal, ordinary, well-functioning pages should have this status code. When it comes to link-related traffic and link equity, it's like nothing you've ever seen before. All that is required of you is to sit back and relax, knowing that everything is just as it should be in the world.
201 - Created
A new resource was created due to the query's success. The user's request created a new resource, such as a page. Before sending 201, the source server must construct the resource. The ETTVI’s status code checker should display 202 if resource creation is not possible at this time.
202 - Accepted
The request was accepted for processing but never completed. The request might be incomplete if it was refused during processing.
When may I use this code? When the server cannot process the request at the time. The client doesn't need to wait for the message to be sent in order to begin the process. Thus a very long process can be begun.
203 - Non-Authoritative Data
The server completed the request properly, but the data sent was not from the primary source (backup, another server, etc.) and hence may be useless. Similar to 200, but indicates that the data was not retrieved from the source.
When may I use this code? Use this code instead of 200 if the sender suspects an external source's response headers differ from the source server's.
204 - No Data
The server sends this code to indicate that the request was received and understood, but no data could be provided to the user. The body of the message should not be included in this code, which is placed after the header in the first line of code that is empty. This allows scripts to run without affecting the document.
When may I use this code? This code allows you to enter or take actions without updating the document.
205 - Reset Content
The server processed the request but returned no content. Unlike 204, this response requires the document to be updated.
When may I use this code? It is usually used when a user fills out a form and sends a request to clean it. Code 204 is similar, but it asks the user to reset the content after completion — for example, to clear the HTML form once a user confirms their submission.
206 - Partially Reset
The server only returns a subset of the content that matches the client's header. Advanced caching techniques employ it when a user requests only a small section of a page's content and the server only responds with data for that region.
When may I use this code? This query is a type of advanced cache validator that is frequently used. In addition, the request should include the area headers that determine the information range that will be returned.
301 - Permanent Redirect
A 301 redirect should be used if a URL has to be permanently redirected to a new one. This means that visitors and search engine bots will be sent to the new URL if they land on the old page. 301 redirects transfer link equity, the weight that your content has gained as a result of the links pointing to it to the new URL. Tests have proven that, despite claims from Google, all 3xx redirects are not processed identically. For long-term page redirects, a 301 redirect is still the best option.
302 - Temporary Redirect
Visitors and bots are forwarded to the new page using a 302 redirect, but link equity may not be transferred. The use of 302 redirects for long-term modifications is discouraged. Search engine crawlers will treat redirects as transitory if they are done with 302s. Therefore the link equity that a 301 passes along will be lost.
404 - Not Found
A 404 error signifies that the server could not locate the requested file or page. There is no way to know if a 404 error means that a website or resource is no longer available or only temporarily unavailable. Type in a URL that does not exist to see what this will look like on your site. A brick wall is what you feel like you've hit. There are many times when a 404 error occurs and the user has no choice but to either try again or leave your site for a different one that provides the information they are seeking.
Some pages on every website will produce 404 error codes. However, redirecting these pages isn't the only method available. One prevalent misunderstanding is that 301 redirecting 404 error pages to the domain's home page is an SEO best practice. In most circumstances, this is a bad idea because it may confuse users who are unaware that the webpage they were trying to reach does not exist.
When ETTVI’s website status code checker shows status code 301, it should be used if the pages returning 404 codes are high-authority pages that receive a lot of traffic or have an evident URL that visitors or links are meant to reach. Sugar-free cupcakes may no longer exist; thus, you can redirect this URL to your sugar-free recipe category page by setting the URL to 301 instead of redirecting it.
It may be necessary for a URL to return a 404 error code in order to prevent search engines from indexing and crawling the URL on a regular basis in order to avoid this from happening. To ensure that your visitors have the best possible experience on your site, Google recommends that you create a custom error page. For example, e-commerce sites frequently produce 404 pages when products are no longer available, making them ideal candidates for a bespoke eCommerce 404 page.
Status Code 410 - Gone
To say the page is gone is more definitive than saying it's been 404ed. Neither the server nor a forwarding address has removed the page. A 410 page redirects visitors and bots away from your site to a dead resource, so if you see a 410 page on your site, remove all references or links to it from your content.
500 - Internal Server Error
When ETTVI’s HTTP header status checker shows a 500 status code, it indicates an issue with the server rather than a lack of pages. A 500 error is a common server problem that will prevent visitors from accessing your website. Whether it's a human visitor or a robot, your link equity will go. As soon as you see any of the following status codes, investigate them and correct them immediately to improve your site's search engine rankings.
503 - Service Unavailable
A 503 response indicates that the server is unavailable, a variation of the 500. Everyone is asked to return at a later time. This could be due to the server being momentarily overloaded or undergoing maintenance. A 503 status code informs search engines that the page or site will only be down for a brief time.
Frequently Ask Questions
What Is the Purpose of an HTTP Response?
How Can I Check HTTP Response Headers?
Use an Ettv’s HTTP Response Checker tool, browser developer tools (Network tab), or command-line tools like curl -I URL. These methods reveal headers like content type, caching rules, and status codes for debugging and SEO analysis.
How Can I Fix a 404 Error?
Fix a 404 error by restoring the missing page, setting up a 301 redirect to a relevant URL, or updating internal and external links. Regularly checking broken links improves the user experience and prevents SEO ranking losses.
What Does a 302 Status Code Mean?
A 302 status code means a temporary redirect, guiding users to a different URL while keeping the original page valid. It does not pass full link equity, making it unsuitable for permanent redirections in SEO strategies.
Can I Use ETTVI’s Status Code Checker For Free?
Yes. People from all around the world can leverage ETTVI’s advanced Status Code Checker to check the http status code and response header for free of cost
Stay up to date in the email world.
Subscribe for weekly emails with curated articles, guides, and videos to enhance your tactics.