A redirect URL automatically forwards users and search engines from one webpage to another. It helps maintain link equity, user experience, and SEO rankings when URLs change or pages are moved.
Redirect Checker
Check Redirect Status Codes; Trace URL Redirections, and Detect Canonicalization in Bulk with Redirect Checker Tool
Redirect Checker Features

Check 301 & 302 Redirect Status Code
Enter URLs in bulk to check their redirect status codes (301, 302)

Redirection Checker
Track the target resource to which the requested URL is redirected with Redirection Checker

Detect Canonicalization
Process the requested URLs to check if they have a canonical tag
Related Tools
ETTVI’s URL Redirect Checker
Check the “Redirect Status Code'' and Trace the “Target URL” in Bulk with Redirect Checker
ETTVI has made it easy for the webmasters to track the http status code of any URL and find out if it is permanently or temporarily moved. In case the URL is redirected, ETTVI’s advanced Redirection Checker too will track the target resource to make sure that it passes full link equity (ranking power) to the right web page. Moreover, to ensure an enhanced user experience on your site, ETTVI’s Online Redirect Checker will find out whether the requested URL is canonicalized or not.
ETTVI’s advanced tool provides quick insights into URL Redirection - it helps to monitor the way a web server complies to the client requests. Leveraging ETTVI’s Redirect Checker, SEOs can easily identify 301, 302, and Meta Refresh Redirects.
ETTVI’s Redirect Checker inspects the requested URL to:
- ➔ Display the Status Code
- ➔ Detect the Canonical Tag
- ➔ Highlight the Target URL
Enter a single or multiple URLs to check redirect status response code; detect canonicalization, and trace URL redirects - for free of cost.
Pro Tip: Canonical Tag is important for SEO and making it wrong can hurt your site’s SEO. Use ETTVI’s Canonical Tag Generator to avoid any kind of human mistake.
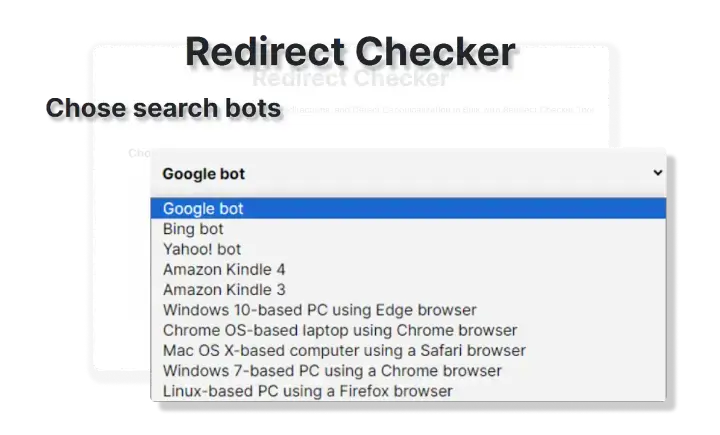
How to Check if a Website is Redirected?
Follow these simple steps to check if a website is redirected with ETTVI’s Redirection Checker:
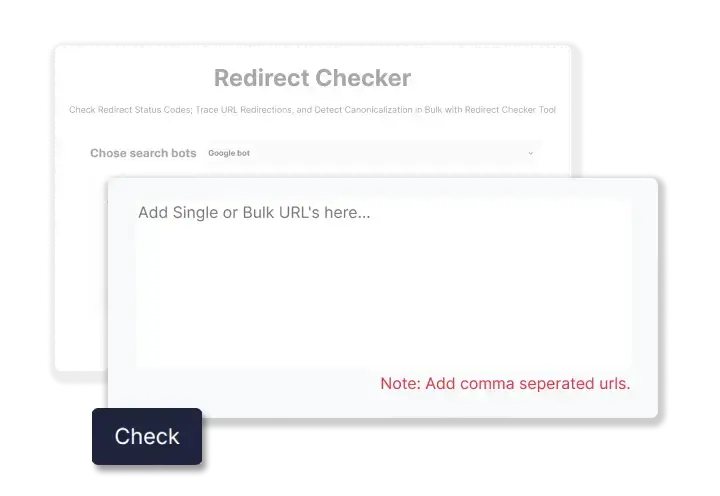
STEP 1 “Enter URL”
Enter the a single or multiple URLs for a quick website redirect test.
STEP 2 “Select User Agent”
To specify the software which is likely to retrieve, render, and display the content of the requested web page(s), choose any of the following user agents:
![]()
STEP 3 “Run the Tool”
Click on ![]() to run ETTVI’s Redirect Checker.
to run ETTVI’s Redirect Checker.
STEP 4 “Check URL Redirection”
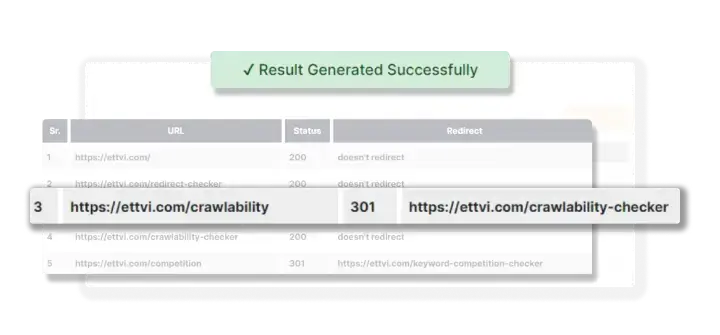
ETTVI’s Redirect Checker will process the requested URL(s) and display the result as follows:
![]()
Why Use ETTVI’s Bulk URL Redirect Checker?
ETTVI’s Redirect Checker is a 3-in-1 SEO tool - it serves as the best URL Redirect Status Code Checker, URL Canonical Tag Detector, and URL Redirect Tracer.
The 301 redirect status code has a different indication and effect as compared to 302 redirect status code. The webmasters can easily perform a redirection test to lookup the response code of a redirected URL and make sure that the web server of the respective resource works fine.
No need to use multiple tools to monitor the redirected URLs when ETTVI’s multi-featured Bulk Redirect Checker monitor and track everything at once. This advanced Redirection Checker Tool identifies the status code of a redirected URL (301 or 302); check if a URL is canonicalized, and discover the resource to which a URL has been redirected.
Yes! All of this can be done at once.
Enter URLs in bulk to keep a check on the redirect status of multiple web resources with ETTVI’s Redirect Checker at a time.
Beginner Guide to Redirect Checker
The HTTP redirect code, abbreviated redirect, move users and search engines to another URL. Redirects are employed when relocating material to a new URL, deleting pages, changing domain names, or merging websites.
What is URL Redirection?
Redirecting a URL to a new location tells computers that a web page has been relocated. You can use redirects to send visitors to the correct page when they visit a page with a redirect. For example, you can tell Google to send its web crawlers to the correct page when they visit a page with a redirect.
A page that has been relocated or removed can be helpful to users who are looking for it. An error like "404 File Not Found" would normally be displayed when a page does not exist. When computers are instructed to load the new location of your page or a linked page, a redirect can be used to instruct them to do so automatically. It's now much more likely that you'll get a response from a potential client after sending them to a blank page than it was before.
404 errors or Broken Links are very dangerous for your website’s SEO and can cause indexing issues. To check all 404 errors in your website, you can use a Broken Link Checker which will help you to identify all 404 errs.
Search engines can benefit from redirects as well. That former page's “link juice” will be lost if it vanishes. In order to preserve the majority of the authority you've built up with Google, you need to set up a URL redirect. Instantly and online, you may do a redirect test using ETTVI's Redirect 301 Checker.
Redirect Types
- 301, or "Moved Permanently," is a suggested SEO practice.
- 302, "Moved Temporarily" or "Found."
- Meta Refresh
301 (Moved Permanently)
Permanent redirects that convey link equity (ranking power) to a rerouted page are known as 301 redirects. For this form of redirect, the HTTP status code 301 points to this. The 301 redirect is the most commonly used mechanism for redirecting a website.
301 redirects are incredibly significant since they convey 90% to 99% of the ranking power to the directed page. This is in addition to making sure that online users and searches can really get to your site.
302 (Found)
In situations where a URL is temporarily redirected, use 302 redirects. According to our research, a 301 is the safest technique to ensure all search engines and browsers provide full credit when permanently redirecting URLs. When it comes down to the specific issue at hand, Google may prefer to see a 301 rather than a 302, even though both can theoretically transmit the same link equity through to the search engine. Using a 302 redirect for a temporary redirect may be the best option.
307 (temporarily relocated)
The HTTP 1.1 successor to the 302 redirects is the 307 redirect. Despite the fact that certain crawlers will treat it as a 302, it is advisable to use a 301 in most circumstances. Only if search engines have previously identified the server as 1.1 compliant and the material is only relocated for a short period of time (like during maintenance). The 302 redirect is the ideal option for information that has been temporarily relocated because it's impossible to tell if the search engines have already indexed the page.
Refreshing the Meta
Meta refreshes are page-level redirects rather than server-level redirects. They tend to be slower, and they're not a good SEO strategy. When used in conjunction with a five-second countdown and the wording "If you are not redirected in five seconds, go here," they are most typically encountered. Even though some link equity is passed along with meta refreshes, they are not suggested as an SEO practice because of their poor usability and the associated loss of link equity.
While the countdown timer is active, advertisements may be displayed, but meta refreshes are normally discouraged. To begin with, visitors may mistakenly believe that your website is insecure, which could damage its reputation. Additionally, if the search engines view the redirect as spam, it could have a negative effect on SEO. This could lead to your website or page being delisted from the search engines.
With ETTVI's redirect chain checker, you can see how a URL is being redirected. Analyze the redirect path of a requested URL to see if it has been redirected. Find out exactly how many times a specific URL has been redirected.
You can use ETTVI’s http redirect checker for free of cost to check your redirects and statuscode with ease.
What is the Purpose of a Website Redirect?
Numerous situations necessitate the usage of domain or URL redirection. For the vast majority of people, the primary reasons are as follows:
- Having content that is twice as long. SEO can suffer if you upload the same thing over and over again. When it comes to SEO, search engines can't decide which URL is the most relevant.
- Keeping track of various websites. A redirect can be used instead of many domains to display a single page.
- The process of changing domains A 301 redirect type can be used to redirect an old domain to a new one permanently. These SEO parameters, such as page authority, are affected by this.
- Changing the URL of a post. When a page is erased, the URL is redirected to a new one, causing the 404 error.
What is the Significance of Redirects?
Seeing an error page when you expect to see a live web page is a bad experience for users. This decreases the number of people who become customers or clients or even email subscribers due to the user leaving the site.
It is not acceptable to serve an error because a link has been relocated or withdrawn.
To ensure that your visitors get to their desired destination, redirect them to the new URL by using a redirect. From page A to page B, you've taken them directly.
It is not uncommon for search engines to remove a page from their index entirely if it produces an HTTP status code of "404".
Search engine bots will need to be informed even if the page has merely been temporarily relocated.
Any backlinks that direct visitors to a non-existent page will not be counted by the algorithm and will therefore be thrown away (this is a real problem). A review of the most prominent brand's websites found literally thousands of fantastic links thrown away due to this issue).
It is possible to lose search engine rankings and dissatisfied customers if redirects are not implemented.
So whether you're redeveloping your website, migrating to a new domain, or simply cleaning up outdated information, you need to know when and how to utilize redirects and which type of redirect to apply.
Use Redirects Only When They're Necessary
Redirects are necessary when:
- You change a web page's URL address.
- You remove the page due to the volume of visitors or backlinks.
- When you redesign your website, the architecture is likely to alter as well.
- You change the domain name of your website.
- There are a variety of ways to integrate multiple websites.
- HTTP to HTTPS conversion.
- If you have URLs with trailing slashes or non-www URLs, you need to ensure that no content is duplicative.
Redirecting just a single URL or directory may be all that is required at times. You may even need to reroute an entire domain at times. As long as you know what you're doing and what your final aim is, you'll be able to employ redirects in a variety of ways.
For example, if you own a company that now only offers a single product online, you may want to consider expanding your offerings. A branded domain name would undoubtedly help you reach more people. But if people type in the old URL, they may not be able to find your new site. Using ETTVI’s site redirect checker, you can rest assured that the traffic to your websites is unaffected. This is the best bulk http status code checker that anyone can leverage for free of cost.
What are the Most Common Ways to Use Redirects?
Based on your server configuration and content management system, redirection can be done in many ways. As a guideline, below are some popular approaches to implement redirects:
- Changing the .htaccess file on your website (when hosted on an Apache server).
- A server block in your nginx.conf file can be included (when the server runs Nginx).
- Using URL redirect and the mod redirect module (when you are on a Lighttpd server).
- Use the 'Easy Redirects Manager' plugin if you're using the WordPress CMS.
- If you have Magento installed, you can use the built-in URL rewrites module.
- Use Shopify's built-in URL redirection mechanism.
- Although meta refresh and JavaScript redirects (and PHP redirects) have been
- mentioned above, they are not advised as an SEO-friendly method of redirecting consumers.
Using Redirects Correctly and Avoiding Typical Mistakes
While the need for redirects is obvious, applying them incorrectly can have a negative effect on both SEO and the user experience. Aware of and working to prevent common problems on your own or your client's sites is essential.
Close Match Content Should Always Be Redirected
It's important to ensure that the new page's content is almost identical to the old page's before redirecting; otherwise, this will be treated as a soft 404 and will be ignored.
In the event that someone clicks the "red dresses" link on a website, they are looking to see if there are any available. If a retailer no longer provides red dresses, redirect customers to a higher dress category.
The website redirect checker from ETTVI is an ideal tool for determining whether or not online links are active. This free application can assist you in determining if any websites have been redirected using pre-defined status codes. Anyone can undertake advanced link analysis with just a few mouse clicks.
Avoid Redirect and Loop Chains
There are two common issues with redirects: chained redirects and loops. According to this report, 8.3% of websites have problems with internal linking errors.
If more than one redirect is required from the original URL to the end URL, this is known as a redirect chain.
You may have previously had a /about-the-company/ page (A) and now have a /about-us/ page (B). A new website has been created, and the URL of this page has been changed to /about (C).
Creating a redirect chain is easy if A redirects to B and B redirects back to C.
These should be avoided at all costs. The current should be updated if they are still in existence (in this example, you would redirect straight from A to C, even if you needed to redirect from B to C.)
A reroute loop is a situation in which it is impossible to go to the intended destination. It's possible that you'd like A to redirect to A, but C also redirects to A. A broken redirect will not direct users or search engines to their intended location, so this should be avoided.
Internal Redirects Should Be Avoided
This can be especially true if you have implemented redirects for a page's URL, which might make it easy to neglect to update internal links.
Given that you have complete control over redirecting internal links, these redirects are unnecessary.
As long as your site has these addresses, it is critical that you regularly update their locations in the site's content so that visitors and search engines aren't accidentally redirected. URL redirect checker from ETTVI is a free tool that lets you see the whole path a redirected URL travels.
Use 302 Redirects Only When Moving Temporarily
301 and 302 redirects are handled differently by search engines, but you still need to think about which one is best for your site.
It is important to avoid using 302 redirects unless the transfer is temporary and will not last for an extended time. Remember that 302 redirects do not disappear from Google's index.
Stopping Duplicate URLs with Redirection
Even if a site has multiple URL variants (non-www, www, HTTPS, etc. ), a simple 301 redirect to the canonical URL can remedy this issue.
Use redirects to avoid having multiple URLs pointing to the same page.
- Non-www and www are both acceptable forms of URLs.
- HTTP and HTTPS.
- URLs ending in a slash (/) versus those that don't
- URLs in both upper- and lowercase
To restore lost link authority and fix linked 404 errors, redirecting is necessary.
Backlinks pointing to a 404 error page are ignored by Google, in case you didn't know.
When you've finished your report, simply click on the Indexed Pages tab and select "Target URL error." Reclaim lost link authority by redirecting to a near match page from a list of URLs with 404's that have links pointing there, which you can now delete and remove.

Frequently Ask Questions
What Does a Redirect URL Do?
Why Is a 301 Redirect Important for SEO?
A 301 redirect permanently transfers link authority to a new URL. It prevents broken links and preserves search rankings. It ensures seamless user navigation and efficient indexing by search engines like Google.
How Can I Check the Status of a Server?
You can check a server’s status using online tools, browser developer tools, or command-line requests like ping and curl. Server response codes (200, 301, 404, 500) indicate accessibility, redirections, or errors.
What Does HTTP Status Code 302 Mean?
A 302 status code indicates a temporary redirection. This means the original URL is still valid. Search engines don’t transfer full link equity, making it ideal for short-term redirects .
Can I Trace URL Redirection?
Yes. ETTVI’s Link Redirect Checker the URL of the resource to which the requested URL has been moved/redirected.
Stay up to date in the email world.
Subscribe for weekly emails with curated articles, guides, and videos to enhance your tactics.