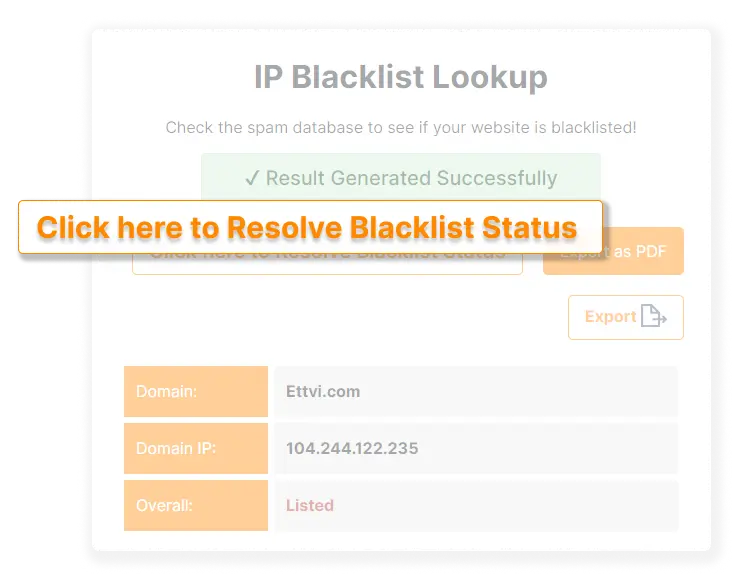
Enter your “Domain Name” or “Domain IP” in the search bar of ETTVI’s IP Blacklist Checker and then press “check”. ETTVI’s advanced tool will lookup the DNSBL database to find the blacklists against which your domain IP is listed.
Features

DNSBL Checker
Search a domain IP through domain name system blacklist database
.svg)
Find Blacklisted Sites
Enter a domain name or domain IP to find if it is blacklisted or not

Quick Results
Takes up a few seconds to detect a domain IP in DNS blacklists
Related Tools
ETTVI’s IP Address Blacklist Checker
Find Out Whether a Domain IP is Listed in the Authoritative Blacklists or NotLookup multiple DNS spam lists at once with ETTVI’s advanced blacklist checker. Just enter a domain name or domain IP to find it in the Domain Name System Blacklist Database.
ETTVI’s IP Blacklist Checker searches through the entire DNSBL database to track the blacklists in which the requested domain name is added. It separately displays the blacklists in which the domain name is found from the blacklist in which it is not added.
Avail of ETTVI’s advanced tool to find the DNS blacklists in which a domain IP has been added as a result of spam history - track the blacklists and it will be easier to find why a website is blacklisted.
How ETTV Checks Blacklisted IP Addresses?
Enter a domain name or domain IP address to check if it is blacklisted or not.
ETTVI’s IP Address Blacklist Checker will search through theDomain Name Systems Blacklist Database to find whether the requested domain name or domain IP is listed in it or not.
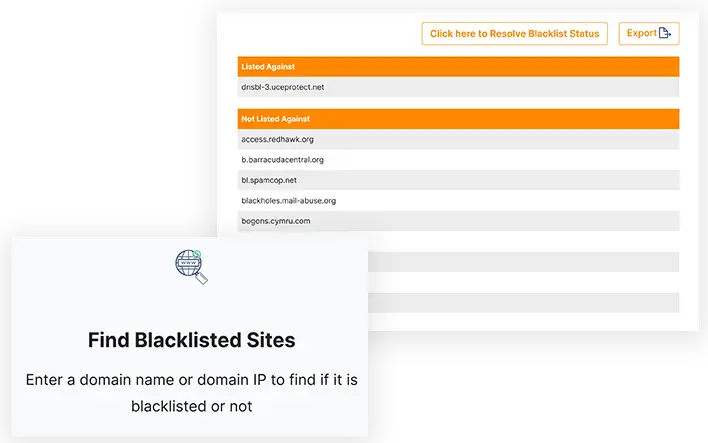
ETTVI’s tool will look up the requested domain in the authoritative DNSBLs, including:
access.redhawk.org
b.barracudacentral.org
bl.spamcop.net
blackholes.mail-abuse.org
bogons.cymru.com
cbl.abuseat.org
cbl.anti-spam.org.cn
cdl.anti-spam.org.cn
combined.njabl.org
csi.cloudmark.com
db.wpbl.info
dnsbl-1.uceprotect.net
dnsbl-2.uceprotect.net
dnsbl-3.uceprotect.net
dnsbl.dronebl.org
dnsbl.inps.de
dnsbl.njabl.org
dnsbl.sorbs.net
drone.abuse.ch
dsn.rfc-ignorant.org
dul.dnsbl.sorbs.net
dyna.spamrats.com
http.dnsbl.sorbs.net
httpbl.abuse.ch
ips.backscatterer.org
ix.dnsbl.manitu.net
korea.services.net
misc.dnsbl.sorbs.net
multi.surbl.org
netblock.pedantic.org
noptr.spamrats.com
opm.tornevall.org
pbl.spamhaus.org
psbl.surriel.com
query.senderbase.org
rbl-plus.mail-abuse.org
dnsbl.justspam.org
rbl.efnetrbl.org
rbl.interserver.net
rbl.suresupport.com
relays.mail-abuse.org
short.rbl.jp
smtp.dnsbl.sorbs.net
tor.dan.me.uk
ubl.unsubscore.com
virbl.bit.nl
virus.rbl.jp
xbl.abuseat.org
xbl.spamhaus.org
zen.spamhaus.org
zombie.dnsbl.sorbs.net
The DNSBL database against which your domain IP is listed and the DNSBL database against which your domain IP is not listed will be displayed in separate sections.
Why Use ETTVI’s IP Address Blacklist Checker?
ETTVI’s IP Blacklist Checker makes it easy for the webmasters to detect a domain in the DNS Blacklist Database. All the SEO can make use of this advanced tool to know why a website IP is blocked so that necessary steps can be taken to remove it from the blacklist accordingly.
It takes only a few minutes to look up a domain name through all the authoritative blacklists - track the spam lists to which the domain IP has been added in real-time.
For sure, ETTVI’s IP Address Blacklist Checker helps the best to lookup domain IP in DNS Blacklist Database and track the Blacklists in which the requested domain is detected as well as the Blacklists in which a domain isn’t found.
With the help of ETTVI’s IP Blacklist Checker, it has become easier and free-of-cost for the webmasters to identify the reason behind the blacklisting of a web resource. The users can easily understand the working of this advanced tool and use it for free of cost.
Beginner’s Guide to IP Blacklisting
A DNS blacklist, or domain name system blacklist, is a software mechanism that assists or facilitates mail server providers in blocking IP addresses that send spam content.
What Is Internet Protocol (IP)?
Before you can grasp an IP address, you need to know what it means to have an IP. Data packets, data formats, or datagrams delivered across a local network or the internet must adhere to the rules of the Internet Protocol (IP). In a dynamic computer network, it is a datagram-oriented and connectionless protocol.
An IP does not rely on a single node or link to function without a central monitor or directory. Because of this, each data packet must include the source and destination's IP address, as well as other critical information, in order for it to be successfully transmitted.
What is an IP Address?
IP addresses are unique identifiers assigned to each machine in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol (IP) to communicate with each other.
IP address Example: 192.16.2.1
It's simple: IP addresses are unique identifiers that allow data to be exchanged between devices on a network or the internet and hold location information, and make equipment easily accessible for communication. Internet Protocol (IP) addresses are an excellent way to distinguish between different types of devices such as printers and PCs. Internet Protocol (IP) addresses are utilised in a variety of ways:
For the purpose of location-finding
Identification of host/network connections
International Internet Protocol (IP) addresses are overseen by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), a government agency. They are managed by five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs), which assign them to local internet registries such as Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and end-users.
What is Blacklisted IP?
IP blacklisting is a technique for preventing malicious or unauthorised IP addresses from gaining access to your computer networks. You can use blacklists to block certain IP addresses or entire ranges of IP addresses. These lists can be used in conjunction with other traffic filtering tools such as firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS).
It is possible to filter out harmful communications by creating and implementing blacklists, which can be applied automatically or manually. The ability to add new addresses to blacklists is common among network security technologies that make use of blacklists. When externally referenced lists are updated, or when the outcomes of an event analysis are analysed, this can be done.
Instantly find out if an IP Address is blacklisted with ETTVI’s IP blacklist checker in anti-spam databases. It aids in the detection of email spam and IP reputation.
5 Challenges of IP Blacklisting
However, blocking certain IPs through blacklisting is not a guaranteed means of preventing unauthorised access to your network. As a result, attackers have come up with a variety of strategies to circumvent blacklisting. The following are a few of these strategies:
IP Address Rerouting
Changing their IP address on a regular basis is a common tactic used by hackers to avoid being flagged as a threat in the first place. In the event that one of their addresses is blocked, criminals may be able to switch to a different one. There's also less of a chance of being prosecuted because of these improvements.
IP Spoofing
IP spoofing can be used in network layer attacks (e.g. DDoS operations that don't require a full three-way TCP connection) to make it look that the attackers are connecting via a different IP address. These people are able to get around the blacklist while maintaining their anonymity because of this. Using this technique, they can fool security systems into believing that compromised credentials are being used legally.
Botnets
End-user devices or Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets can be included in enormous botnets operated by a number of hackers. In many situations, these devices are hacked and taken over by the attackers or rent a botnet service on the dark web.
Many attacks now use enormous numbers of IP addresses that often vary as devices join and depart botnets. IP blacklists are powerless in the face of such an onslaught.
False Positives
Another problem you may have while creating blacklists is the issue of false positives. Despite the fact that these issues aren't directly related to attackers or security, they can nonetheless have an impact on productivity.
Incorrect IP detection
Multiple users of the same IP address provide an additional problem. There is no way to tell who is currently utilising a given IP address when dynamically issued to users. To put it another way, if you decide to ban someone because of their aggressive behaviour, you may inadvertently stop someone else from accessing your network down the road. Your domain or IP address should be checked with ETTVI’s free blacklist checker against common blacklist databases to make sure they aren't on any of them. If your resources appear on the list, there is no need to be concerned.
How Do IP Addresses Work?
Using an IP address is similar to using a home address. Your home address must be provided if you want to receive mail or a package from a courier. As with electronic mail and web data, the sender must identify you and your connected device or computer to transfer data. Your computer, tablet, smart lighting, smartphone, thermostat, baby monitor, or any other internet-connected device requires an internet number or address to connect and communicate with other devices.
An IP address is not a random number; it is generated mathematically and assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
The IP address 192.16.2.1 is represented as a set of four integers separated by a period in the preceding example. This set has a range of 0 to 255 for each number. IP addresses can therefore range from 0.0.0.0 through 255.255.255.255.

IP Addresses of Several Types
Different sorts of IP addresses can be found in each category.
Private and Public:
Private and public IP addresses are available to businesses and individuals who use the internet. The IP addresses are determined by network location. You can utilise a private IP address in your home or office's computer network. Your router assigns a unique IP address to each connected device (computer, smartphone, speakers, smart TV).
The number of IP addresses in residence grows as the number of devices used grows. It's important for your router to be able to identify between the many systems on your local network, so it generates unique private IP addresses for each of them. The private IP addresses will not be accessible to devices outside of the private network.
IP addresses that are utilised outside of your home or workplace computer network are referred to as public IP addresses. The Internet Service Provider (ISP) assigns a unique IP address to any device that connects to the public network or the Internet (ISP). Your router is assigned a public IP address by your ISP, which has a large number of IP addresses to choose from. To find your device on the internet, external devices need public IP addresses. There are two sorts of public IP addresses: static and dynamic.
Static vs Dynamic:
IP Addresses that Cannot be Accessed With a Dynamic IP Address
They don't change often or automatically, yet they always remain the same. Internet service provider (ISP) IP addresses do not change.
Every firm or individual does not need a static IP address. You'll need a static IP address if you want to run your own server. It is possible to maintain a consistent IP address for all of your online accounts by making use of static IP addresses such as those found in your email and website domains. As a result, third-party devices with access to the internet can easily locate you.
Making use of an IP Address that is Constantly Changing
Using an internet service provider means an IP address will be assigned to you from a pool of potentially available addresses. The IP address assigned to a customer remains in effect as long as the customer is connected to the internet. As a result, when consumers stop using the internet, their given IP address becomes available to other users. The IP addresses of static hosts, on the other hand, do not change over time. These dynamic addresses are given to other customers and can be reallocated at any time.
IP addresses can be re-established using this method without the need for any further work by ISPs. Additionally, hackers are unable to identify a specific user because their IP addresses are constantly changing.
Many people have advocated the use of static IP addresses for organisations looking to host their own websites. In the same way, there are two types of IP addresses for websites. You can use ETTVI's IP Blacklist Checker to see if several anti-spam databases have blacklisted your IP address. There are a number of prominent databases that track IP addresses that have been blacklisted.
IP Addresses that are Shared or Dedicated
Shared IP Address: If you use a web host's shared hosting option, you'll be sharing a server with other websites. It's ideal for sites with low traffic, like blogs and portfolios. They will all share the same IP address.
Dedicated IP Addresses:Dedicated hosting plans are a good choice for larger companies looking for a more secure alternative and professional gamers who want more control over their servers. A dedicated IP address can be purchased by them. You can quickly purchase SSL certificates and run your FTP server using this software. As a result, you have the option of securely sharing files within your company or remaining anonymous. It's also possible to use your IP address instead of your domain name to access your site.
What Are IP Address Subnets and Classes?
Subnetworks
Both IPv4 and IPv6 networks can be broken down into subnetworks. IP addresses are made up of two parts:
Prefix in the Upper Bits of the Network
A subnet mask or CIDR notation is used to divide an IP address into its host and network portions in a subnetwork. A "subnet" refers to an IPv4 subnetwork. However, CIDR nomenclature and principles are used in both versions.
Slash (/) at the end of an IP address is used in subnets to signify the network portion or routing prefix. The majority of subnet masks begin with 255 and go on until the network segment is complete.
This is an IPv4 address with the subnet 255.255.255.0 assigned to it, and it has the IP address 172.0.2.1 in its subnet. 172.16.2.1/24 can be used as a CIDR notation for this. The first 24 bits of an IP address represent the subnet and network in this case.
Class of IP Addresses:
The network had the highest-order octet at first, but it was later reduced. As the number of networks grew, the 256-network limit became insufficient. Classful network design was introduced as a result of this change.
With this concept, subnetwork architecture could be fine-grained, and a bigger number of networks could be assigned. When an IP address was created, the first three bits of the most important octet were used to identify its "class." A, B, and C were the three classifications that were defined.
IPv4 also allowed addresses between 0.0.0.0 and 255.255.255.254, which is the range of IPv4 addresses. But on TCP or IP networks, some numbers are reserved for specific uses. The IANA is aware of these concerns. They can be broken down into the following categories:
Shows a device's connection to an IP and TCP network by using the default IP and TCP networks.
For network broadcasts that must be received by all computers on a network, use 255.255.255.0.
A machine can use 127.0.0.1 to see if it has been issued an IP address or not.
If you're trying to receive an IP address via DHFC servers, you'll get 169.254.0.1-169.254.255.254, which is the Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) pool of IP numbers. In order to determine if your mail server IP Address is banned in any RBLs, ETTVI's IP Blacklist Checker program can be used (Realtime Blacklist). Many RBLs will be able to check your IP address.
All other IP Addresses are in Subnet Classes
An address system for computers in the subnet, which is connected to a larger network via a router, enables the communication between computers in the subnet without transferring any data over the more extensive network. It is also possible to designate a router to identify subnets and route traffic accordingly.
Frequently Ask Questions
How Do I Check If My IP is Blacklisted?
How Does ETTVI’s IP Blacklist Checker Work?
ETTVI’s IP Blacklist Checkers lookup the requested domain name or domain IP in the DNSBL database to find out if it is listed against a blacklist or not.
What Does It Mean If IP address is Blacklisted?
IP blacklisting enables the webmasters to block the IP addresses which send malicious and harmful data to their network or web resources.
Why Do You Need ETTVI’s Blacklist Checker?
ETTVI’s Domain IP Blacklist Checker enables the webmasters to find out why a domain has been blacklisted as it displays the authoritative blacklists in which it is added. This helps the webmasters to troubleshoot it and remove the IPs from the DNSBL database.
Is ETTVI’s IP Blacklist Checker Free?
Yes. ETTVI’s Domain IP Blacklist Checker is free of cost. People from all over the world can access and use it to lookup a domain IP in DNSBLs.
Stay up to date in the email world.
Subscribe for weekly emails with curated articles, guides, and videos to enhance your tactics.